
Meir, Yigal
Strongly correlated and topological systems. Mesoscopic systems; Disordered systems; Biology and Ecology.

Cohen, Doron
Quantum chaos; Driven mesoscopic systems; Interplay of stochastic and coherent dynamics.

Schechter, Moshe
Glasses; Disordered systems; Quantum magnetism.

Grosfeld, Eytan
Topological super conductors; Topological insulators; Non-Abelian anyons.

Meidan, Dganit
Topological phases of matter; interactions in lowdimensional systems.

Bar Lev, Yevgeny
Condensed matter theory, thermalization, nonequillibrium

Bel, Golan
Equilibrium and Non-equilibrium statistical physics; Single molecule spectroscopy; Non-linear dynamics; Climate predictions.

Aharony, Amnon
Condensed matter theory; Spintronics.

Avishai, Yshai
Condensed matter physics; Mesoscopic systems; Transport properties in one and two dimensional systems.

Ben-Abraham, Shelomo Izhaq
Ordered aperiodic structures such asquasicrystals and modulated crystals.

Entin-Wohlman, Ora
Condensed matter theory; Spintronics.

Horovitz, Baruch
Superconductivity; Phase transitions of fluxlattices; Josephson junctions. For a complete list of publications please visit my homepage.

Golub, Anatoly
Quantum Hall effect; Hall effect in unconventional superconductors.
Research highlights
Electronic Transport in the Nano-Scale (Meir's Group)
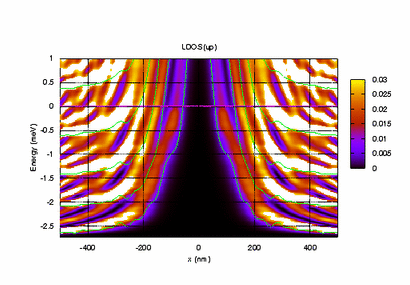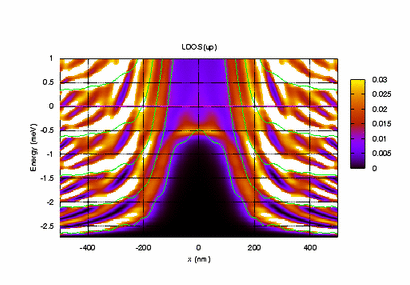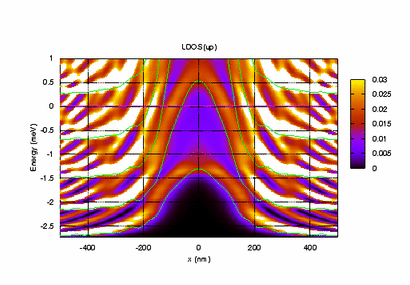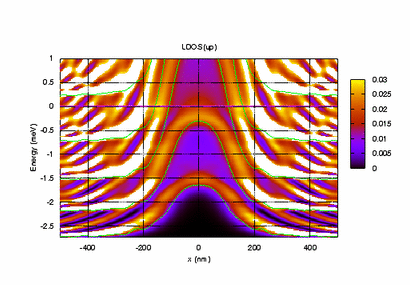
As electrons are confined to smaller and smaller spaces, quantum effects and strong correlations among the electrons start to dominate the underlying physics. In this area of research we investigate how such effects influence the electronic properties of miniaturized devices, such as quantum dots (QDs) and quantum point contacts (QPCs), and how such devices can be used to enhance our understanding of quantum mechanics and many-body physics.
Disordered Superconductors (Meir's Group)
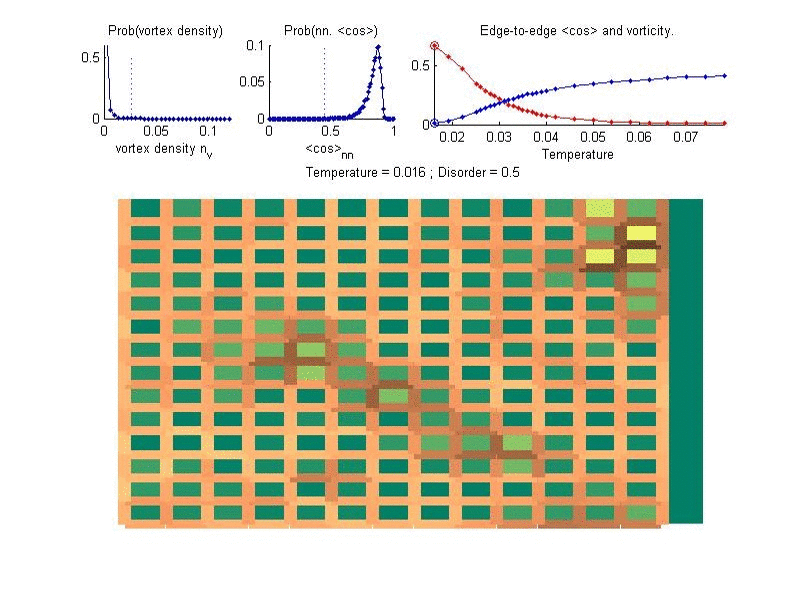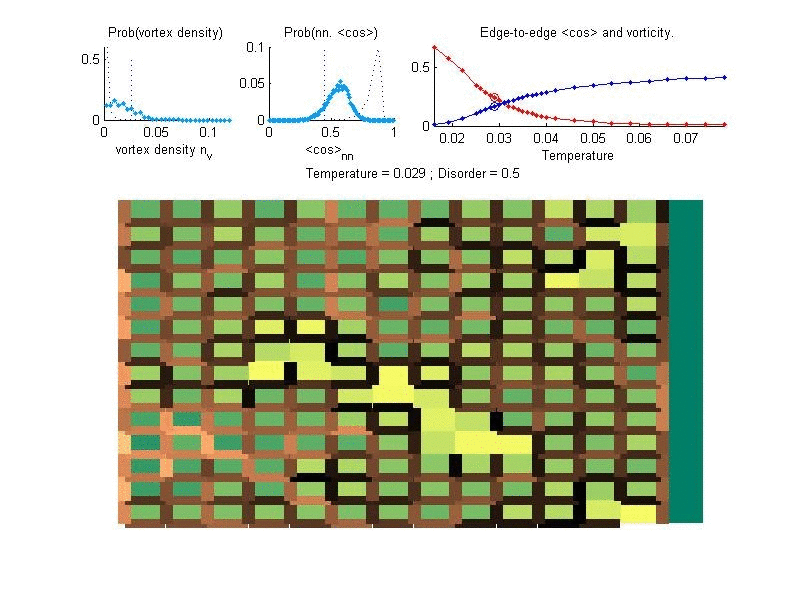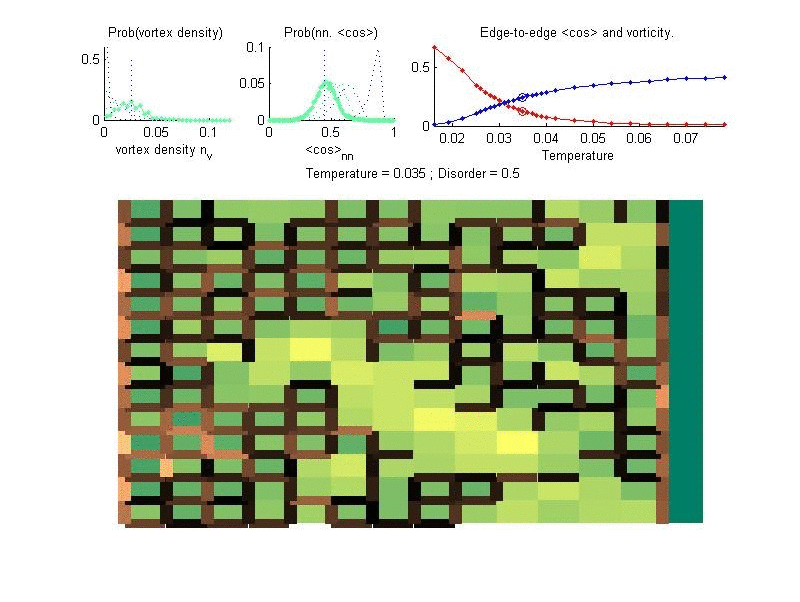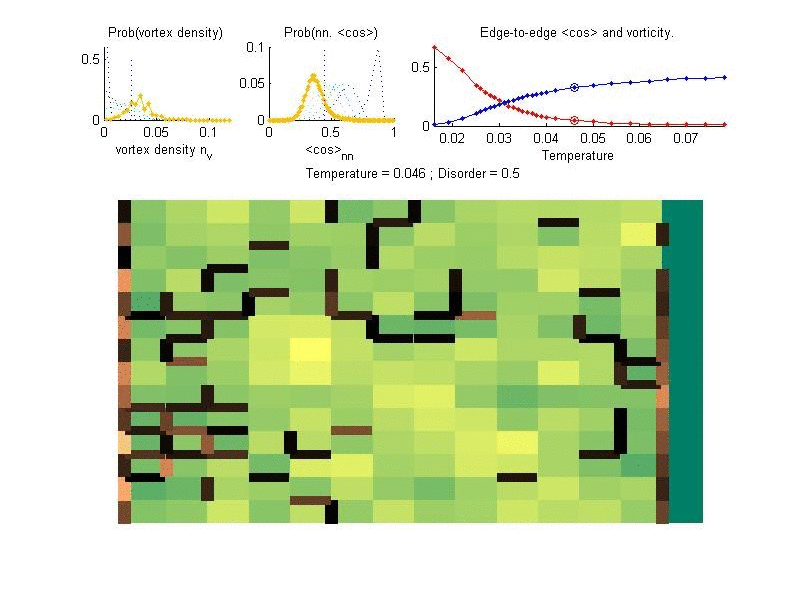
In superconductors electrons can flow without any resistance. In reduced dimensions, superconductivity is highly influenced by geometry and disorder, in a way which is very different than the expectations from the standard BCS theory of superconductivity. We investigate the interplay of geometry, disorder and superconductivity, in order to explain numerous intriguing experimental observations, and to predict novel phenomena.
Superfluidity and thermalization in low dimensional Bose-Hubbard circuits (Cohen's Group)
Circuits with condensed bosons can support superflow. Such circuits, if realized, will be used as QUBITs (for quantum computation) or as SQUIDs (for sensing of acceleration or gravitation). We are studying the feasibility and the design considerations for such devices. The key is to develop a theory for the superfluidity in an atomtronic circuit. Such theory goes beyond the traditional framework of Landau and followers, since is involves ''Quantum chaos'' considerations.
Non-equilibrium steady state of low-dimensional systems (Cohen's Group)
It is possible to induce non-equilibrium steady state current, which required e.g. a radiation source. We have studied the non-monotonic dependence of the current on the intensity of the driving, and its statistical properties. We also have addressed questions that concern the relaxation of such current, and how it depends on percolation and localization properties of the model.
Topological Supercoductors and Majorana Fermions (Grosfeld's Group)
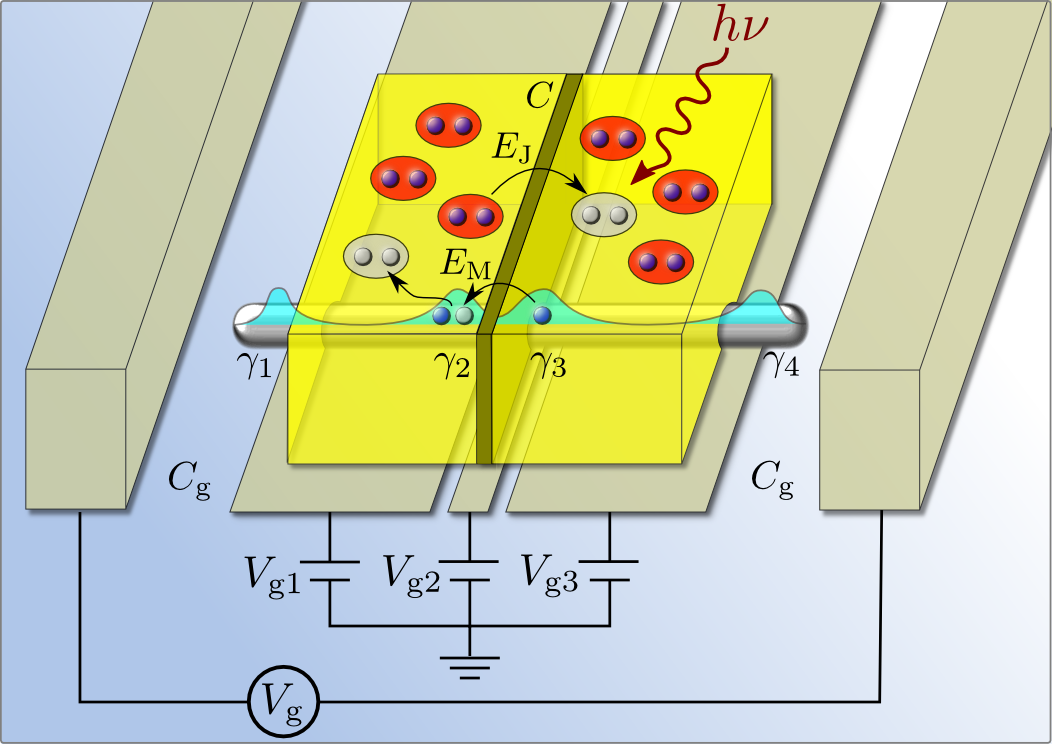
We are interested in properties of topological superconductors, a fascinating state of matter that could be harnessed to create a new type of quantum computer [E. Ginossar and E. Grosfeld, Nature Communications 5, 4772 (2014), Tunability of microwave transitions as a signature of coherent parity mixing effects in the Majorana-transmon qubit.]
Nonequillibrium dynamics (Bar Lev's Group)
While conventionally condendsed matter theory was moslty concerned with equilibrium or stationary states situations, recent theoretical and experimental progress spurred interest in nonequillibrium. In our group we study various situations of nonequillibrium dynamics, such as transport, quenches and external driving.
Disordered Systems (Bar Lev's Group)
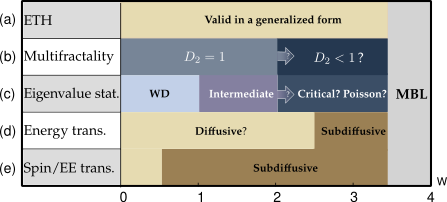
Disorder allows avoiding thermalization and defy conventional statistical mechanics, through the mechanisms of Anderson or many-body localization. We study these ergodicity breaking mechanisms in detail. In particular the nature of transport and correlations spreading in systems on the verge of localization.
Dynamics and escape of active particles (Bel's Group)
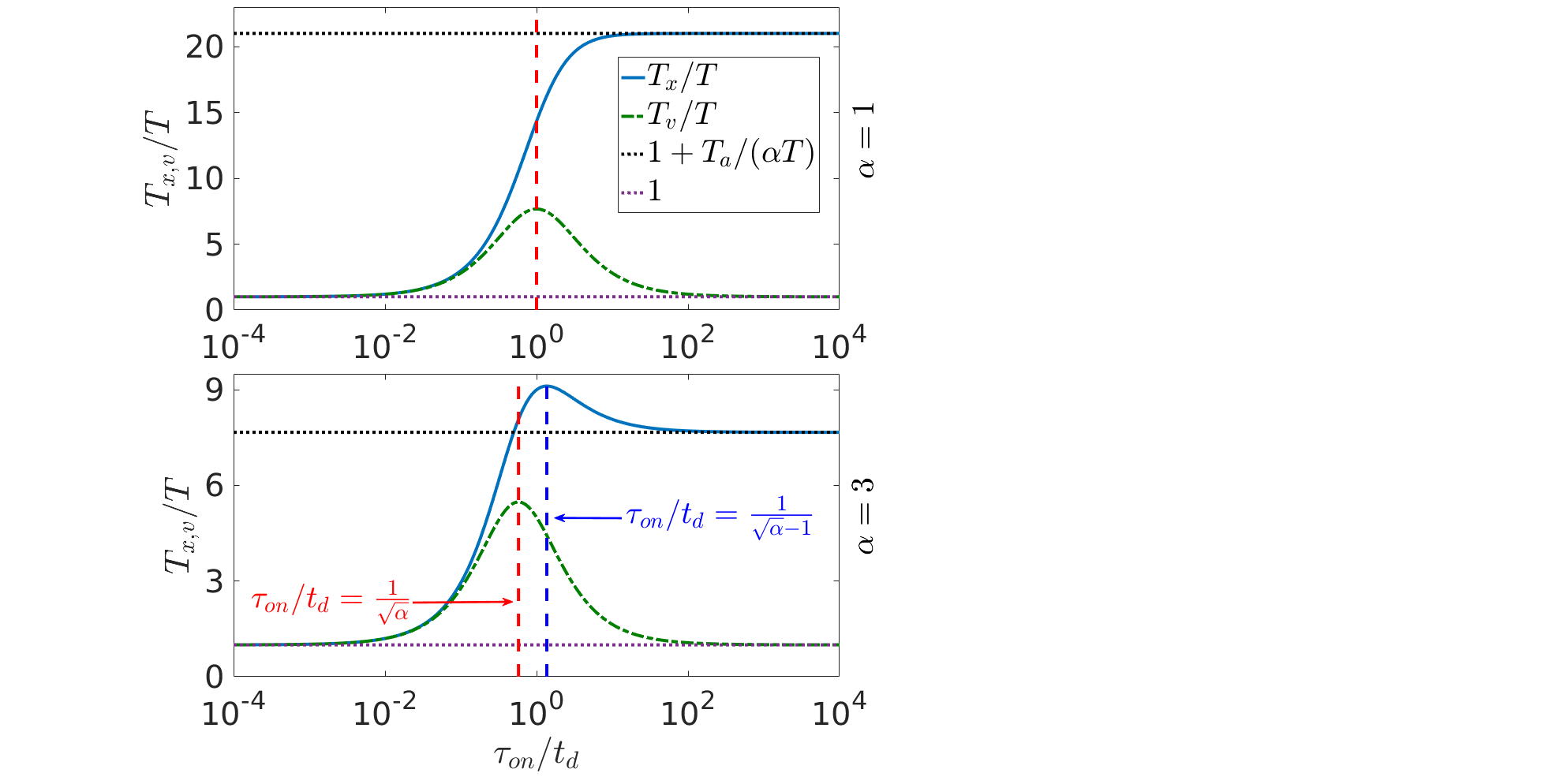
The dynamics of active particles is of interest at many levels and is the focus of theoretical
and experimental research. There have been many attempts to describe the dynamics of particles
affected by random active forces in terms of an effective temperature. However, there in no unique definition of the effective temperature. We study the dynamics of trapped particles subjected to both thermal and active forces. We found that over a large fraction of the parameter space, the potential
energy effective temperature may be used to describe the escape process of trapped active particles. The results are relevant to many systems ranging from the dynamics of bacteria to sheared glasses.
Spin related mesoscopics (Aharony's Group)
*** Quantum mechanics of nanometer sized devices: using electron wave interference to manipulate electron motion.
*** Spintronics: taking advantage of the electron’s magnetic moment (spin), and not only of its charge, to store and read information. Possible applications in quantum computers.
*** Multiferroic materials are both magnetic and ferroelectric, and therefore can be manipulated by both electric and magnetic fields.
Mesoscopics (Entin-Wohlman's Group)
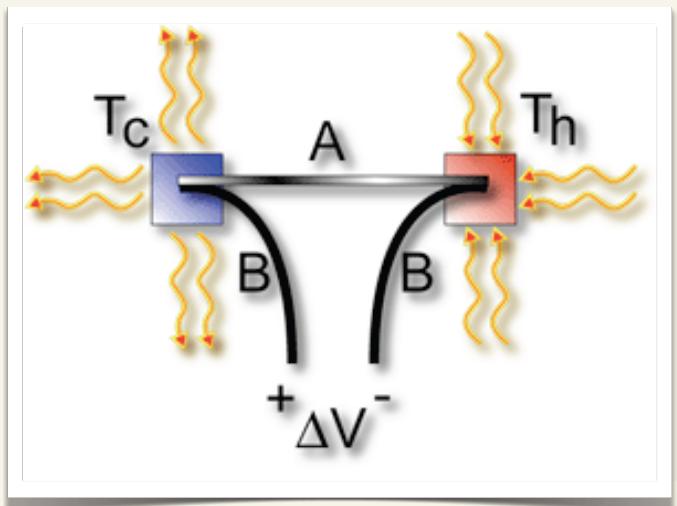
*** Molecular junctions and thermoelectricity: studying transport of electrons and of heat through single-molecule bridges (e.g. nano-tubes). Finding bounds on the thermoelectric efficiencies.
*** Superconducting-insulator transition: studying the way the conductance of hybrid systems are modified as part of the sample goes superconducting.
*** Persistent current in metalic rings: Superconducting fluctuations generate persistent currents around rings even above the superconduction temperature, which may be reduced by proximity to normal metals.