Astrophysics and Cosmology
Space Weather

Michael Gedalin
magnetic reconnection
The Sun governs the life of the Earth. Solar-terrestrial relations occur not only via radiation coming to the Earth but also via time-varying plasma flow. This solar wind is decelerated and diverted by the bow shock forming at the distance of about 10 Earth radii toward the Sun. The diverted plasma flows around the Earth, shaping a magnetosphere with a long tail and a current sheet where the so called "magnetic reconnection" (see movie) occurs, causing magnetic substorms. We study the basic processes in this interaction.
Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics
Quantum Cheshire Cat

Daniel Rohrlich
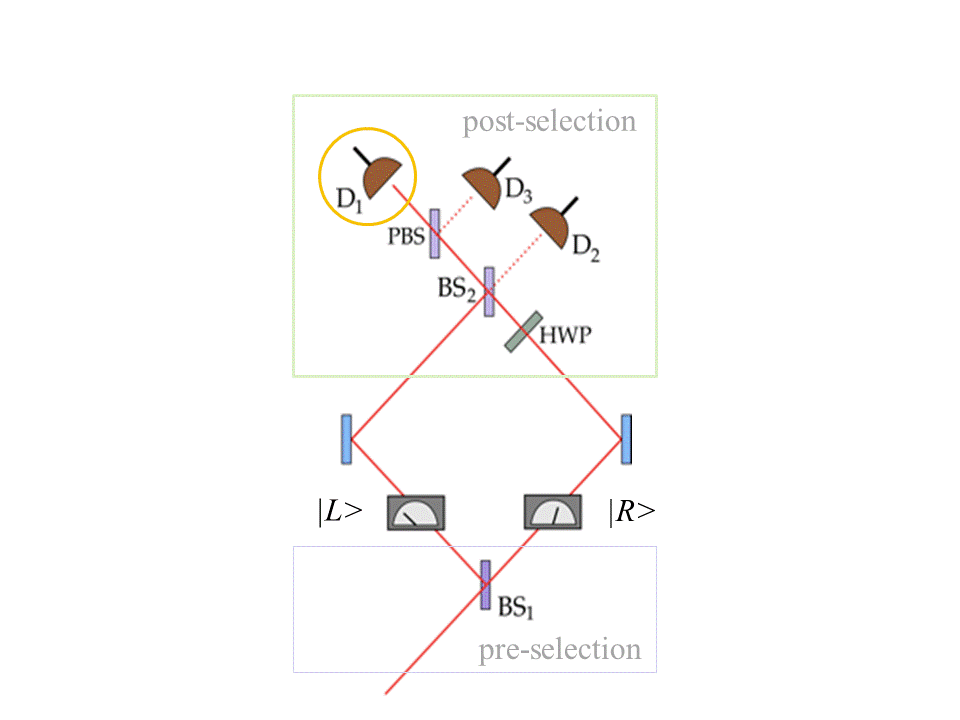
If D1 clicks, then intermediate measurements find the Cat (photon) in |L> while its grin (polarization) is nonzero only in |R>.
Y. Aharonov, S. Popescu, D. Rohrlich and P. Skrzypczyk, "Quantum Cheshire Cats", New J. Phys. 15 (2013) 113015. We present a quantum Cheshire Cat. Weak measurements on a pre- and post-selected ensemble find the Cat in one place and its grin in another. The Cat could be a photon, with circular polarization as its quantum "grin" state. But see T. Denkmayr et al., "Observation of a quantum Cheshire Cat in a matter-wave interferometer experiment", Nat. Comm. 5, 4492 (2014); they send neutrons through a silicon crystal interferometer, while weakly probing their locations and magnetic moments. The results suggest that the neutrons go along one beam path while magnetic moments go along the other.
Biological and Soft Matter Physics
Soft Matter Physics and Renewable Energy

Arik Yochelis
Simulation of self-assembled nano-structure in a model for ionic liquid
Most renewable energy devices exploit nano-scale morphologies that are paramount to large surface area, required to increase activity. However, electrical effects are often strong enough to influence the structure of active layers of those materials leading to a notorious decrease in performance. To date, theoretical studies have dealt almost exclusively with uncoupled models of self-assembly and electrokinetics. We develop novel and computationally amenable mean-field frameworks that do unify them. Our expectations are to advance devices, such as batteries, supercapacitors, and solar cells.
Condensed Matter Theory
Disordered Systems

Yevgeny Bar Lev
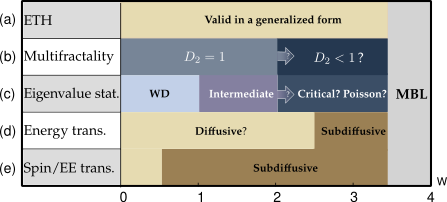
Characterization of the anomalous ergodic phase, leaves many questions open.
Disorder allows avoiding thermalization and defy conventional statistical mechanics, through the mechanisms of Anderson or many-body localization. We study these ergodicity breaking mechanisms in detail. In particular the nature of transport and correlations spreading in systems on the verge of localization.
Condensed Matter Experimental
Magnetic Resonance on the single atom level

Yishay Manassen
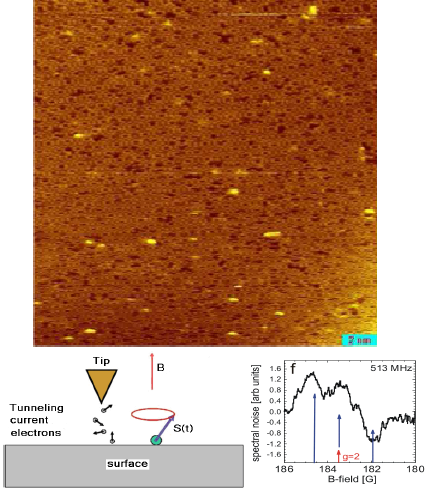
above-silicon surface with carbide spots below tunneling junction and spin - spectrum
In the STM image shown, observed in our lab, we see some disordered white spots. The STM does not have chemical identification capability. Such chemical identification is observed macroscopically using macroscopic magnetic resonance – both of electrons and nuclei. We develop a magnetic resonance technique on the single atom level, observed via a Larmor frequency component in the tunneling current. We identify the type of atoms under the tip using their spectrum – for example the SiC hyperfine spectrum. Preliminary results showed the observation of the nuclear transitions (NMR) with the STM.
High-Energy Physics
Cosmology

Ram Brustein
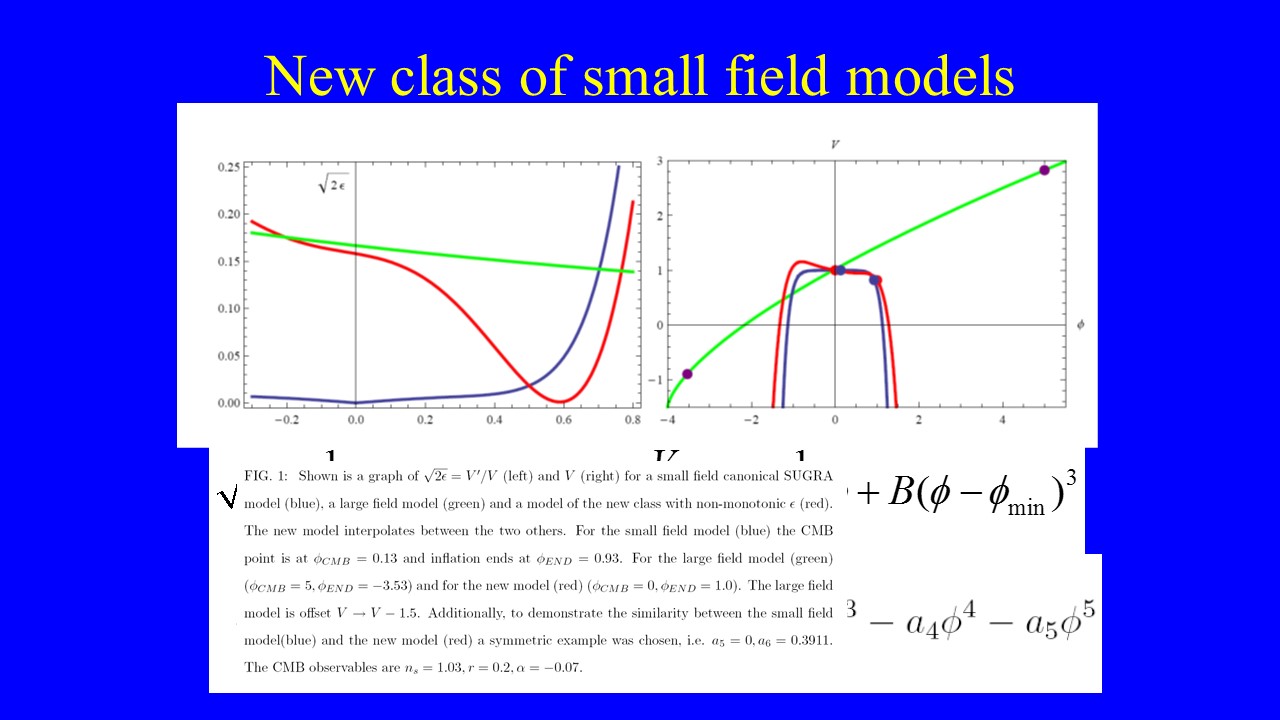
A new class of cosmic inflation models
The early universe is used as a theoretical laboratory for studying fundamental physics, the laws of gravity and quantum mechanical aspects of matter under extreme conditions. We study models of cosmic inflation in the early universe and dark energy in the late universe and their possible realizations in quantum field theory and string theory models. Our recent research focuses on models of high-scale inflation which produce an observable signal of gravitational waves in the cosmic microwave background.